The cochlea
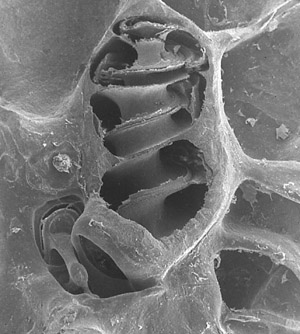
The left image shows the bony wall of the cochlea has been cut away revealing the fluid filled spiral chambers within. The last of the three ossicular bones, the stapes, fills the oval window of the cochlea.
The right image shows a surface view of the apical turn of a chincilla cochlea. The organ of Corti can be seen spiraling downwards in a counter-clockwise direction (indicating that this is a left cochlea, a right cochlea spirals downwards in a clockwise direction).
The “hole” which is located in the centre of the spiral is the heliocotrema, where fluids from the scala vestibuli and scala tympani meet.
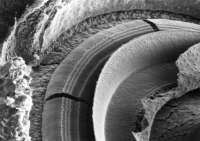
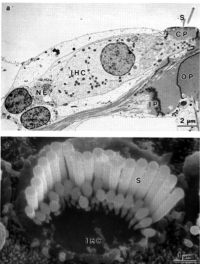
Image A shows a surface view of the chinchilla organ of Corti showing, from left to right: the bony wall; spiral ligament and stria vascularis; hair cells; tectorial membrane; Reissner’s membrane; modiolus.
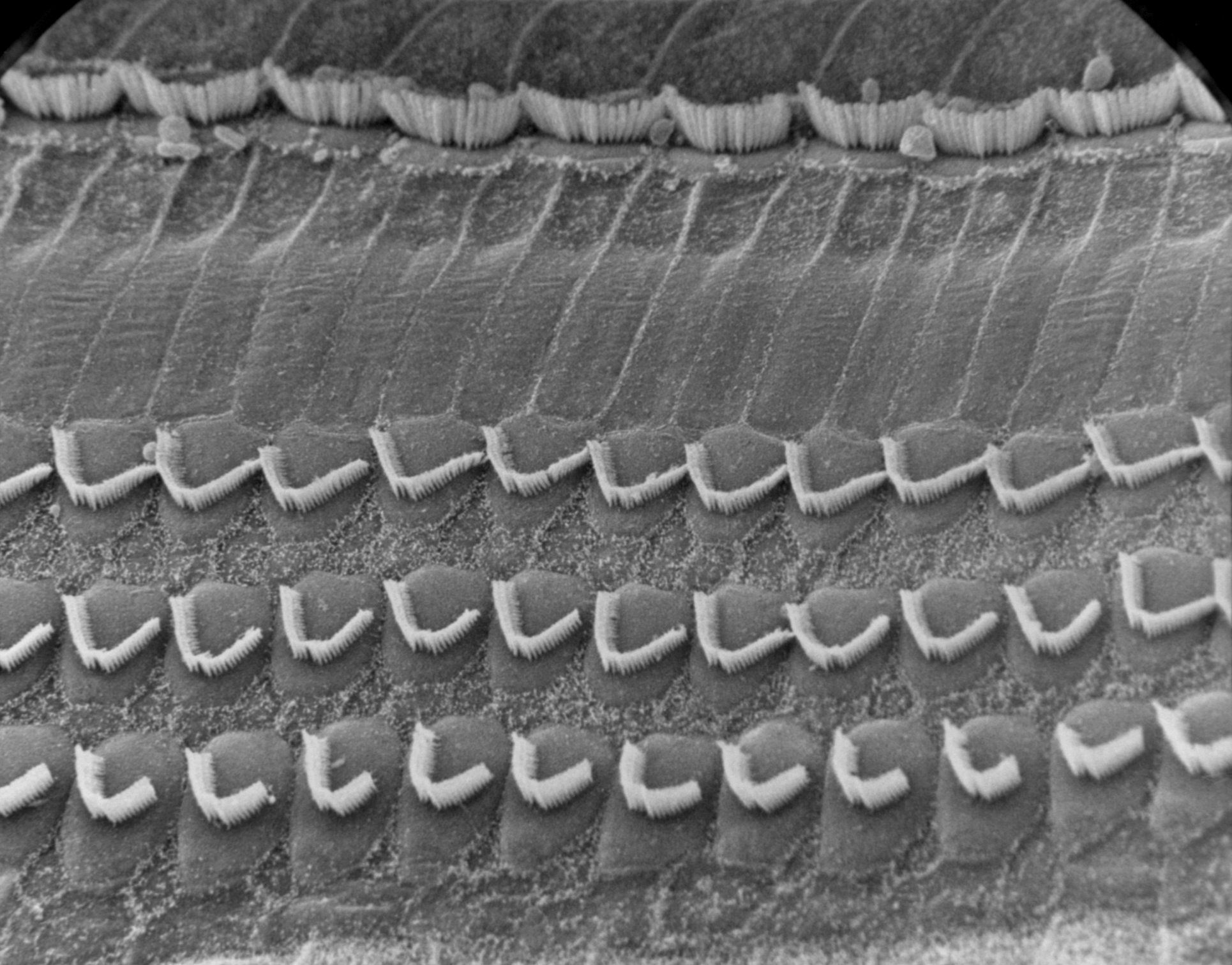
Image B shows the sensory surface of the organ of Corti. Three rows of outer haircells and one row of inner hair cells are seen.
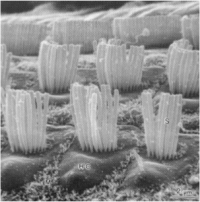
Image C shows a close up of the sensory outer hair cells.
Image D is a close up of the inner hair cell.