Our team is using advanced magnetic resonance (MR) and neurophysiological techniques to understand the causes of brain injury and promote optimal neurodevelopment in high-risk newborns. Our multidisciplinary research team includes clinicians, physicists, statisticians, researchers, nurses, allied health professionals and experts in brain imaging and monitoring. We also collaborate with Neonatal Neuroscience groups around the world. As a team, we work to improve brain health outcomes in the following vulnerable populations:
Neonatal Neuroscience
NeoNs
The brain develops rapidly during the third trimester of pregnancy and in the first months of life.
Preterm newborns
In our studies of preterm neonates, we are asking questions such as:
- Why does white matter injury occur?
- How can we optimize development in preterm infants?
- What impact does infection have on the epigenome?
- How can we protect the brain from pain?
- Does nutrition during the perinatal period impact development?
- How can we use neuroimaging to predict developmental outcomes?
Term newborns
We study term-born babies in the neonatal intensive care and cardiac critical care units, asking questions such as:
- What influences abnormal blood sugar have on brain development in newborns with early signs of distress?
- Why some newborns with heart disease acquire brain injury and others do not?
- How does heart function affect fetal and neonatal brain development?
- How can we optimize brain development in babies with congenital heart disease?
- How can we study fetal cardiovascular physiology using MRI?
How we study the brain
Advanced MRI
MRI is used to take a detailed pictures of the baby’s brain. Study participants have MRIs during periods of critical brain development such as: while they are still in utero, when they are first born, when they reach term age and/or around clinical interventions such as therapeutic hypothermia or cardiac surgery. Our research scans are done without sedation using the feed and sleep technique.
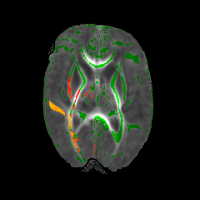
MRI analysis techniques
Using advanced magnetic resonance (MR) techniques we can visualize functional brain networks, microstructural volumes, neural metabolites, white and grey matter pathways and markers of brain maturation. We use these tools to identify clinical factors that affect the brain.
Neurophysiological testing
Some studies involve continuous video (cEEG) and amplitude-integrated electroencephalography (aEEG) as a non-invasive measure of brain activity. EEG is used to quantify brain electrical activity at critical points in neonatal development, diagnose seizures and holds prognostic significance.

Long-term follow up
As study participants grow, they are followed by the Neonatal Follow Up Teams at each of our study sites. Using standardized scales of developmental outcomes including motor, language, visual, and cognitive abilities are assessed at defined time points. Parents also complete surveys and questionnaires about their child’s behavourial development.
