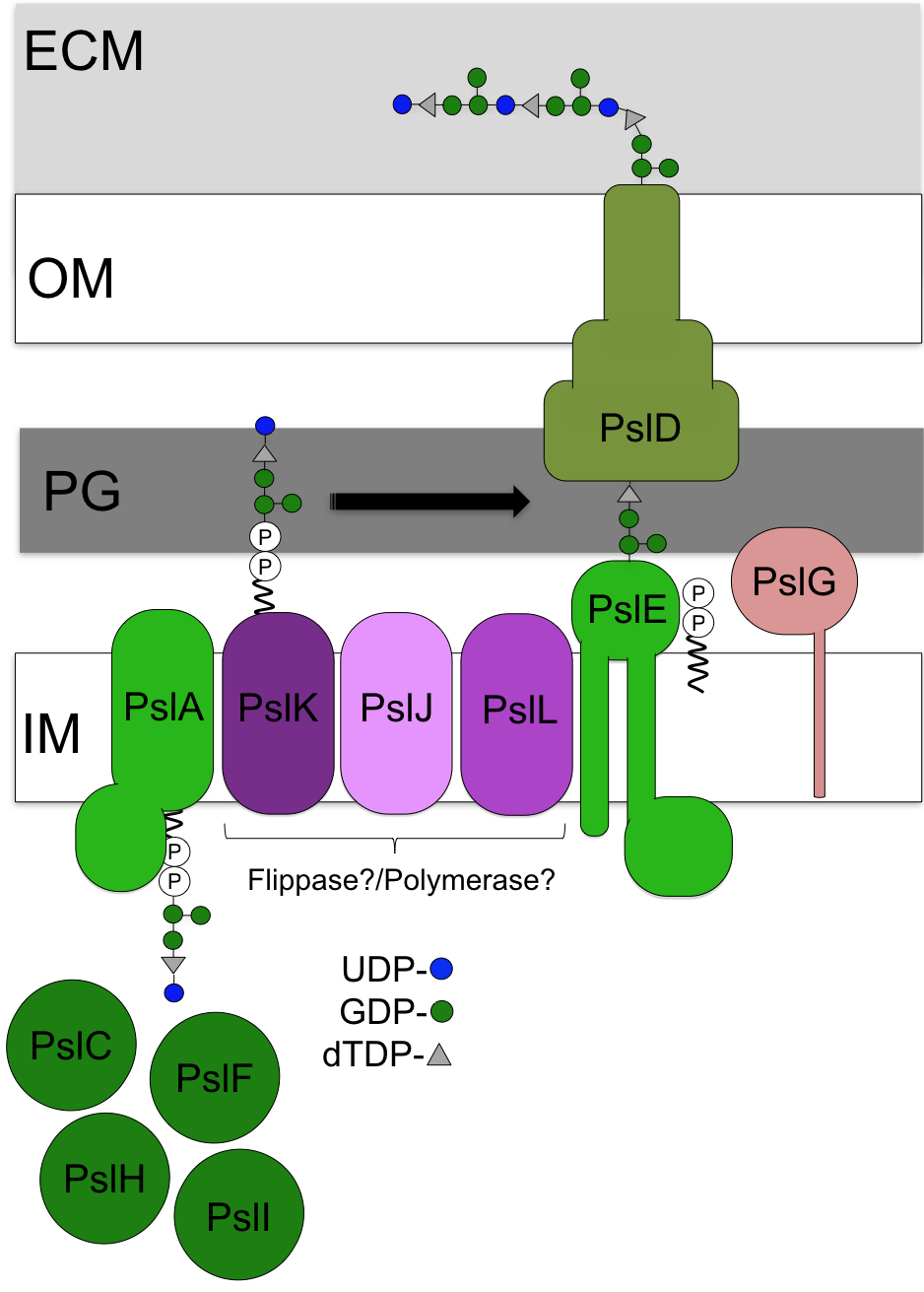
Psl is the predominant polysaccharide found in biofilm infections in clinical and environmental settings. Psl acts as an adhesin and plays an important role in the formation and maintenance of the biofilm architecture in P. aeruginosa infections. The polymer provides protection against the immune system and is a first line of defense during the initial stages of biofilm development. PSL is composed of a pentasaccharide-repeating unit of D-mannose, D-glucose and L-rhamnose. While the mechanistic details of how the polymer is produced are not fully defined, it is proposed to occur via a Wzx/Wzy-dependent mechanism, similar to the E. coli group 1 capsular polysaccharides.
We have recently shown that deletion of pslG does not impact Psl synthesis or biofilm formation and have demonstrated that PslG is an active glycoside hydrolase.
Current projects
Ongoing projects are focused on:
- Determining the role of the PslG in polymer biosynthesis.
- Developing PslG as a therapeutic for the prevention and degradation of PSL-dependent biofilms.
Selected Publications
- Characterization of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa Glycoside Hydrolase PslG Reveals That Its Levels Are Critical for Psl Polysaccharide Biosynthesis and Biofilm Formation. Baker P, Whitfield GB, Hill PJ, Little DJ, Pestrak MJ, Robinson H, Wozniak DJ, Howell PL. J Biol Chem. 2015 Nov 20;290(47):28374-87. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.674929.
- Biosynthesis of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa Extracellular Polysaccharides, Alginate, Pel, and Psl. Franklin MJ, Nivens DE, Weadge JT, Howell PL. Front Microbiol. 2011 Aug 22;2:167. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2011.00167.
- The Pel and Psl polysaccharides provide Pseudomonas aeruginosa structural redundancy within the biofilm matrix. Colvin KM, Irie Y, Tart CS, Urbano R, Whitney JC, Ryder C, Howell PL, Wozniak DJ, Parsek MR. Environ Microbiol. 2012 Aug;14(8):1913-28. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2011.02657.x.