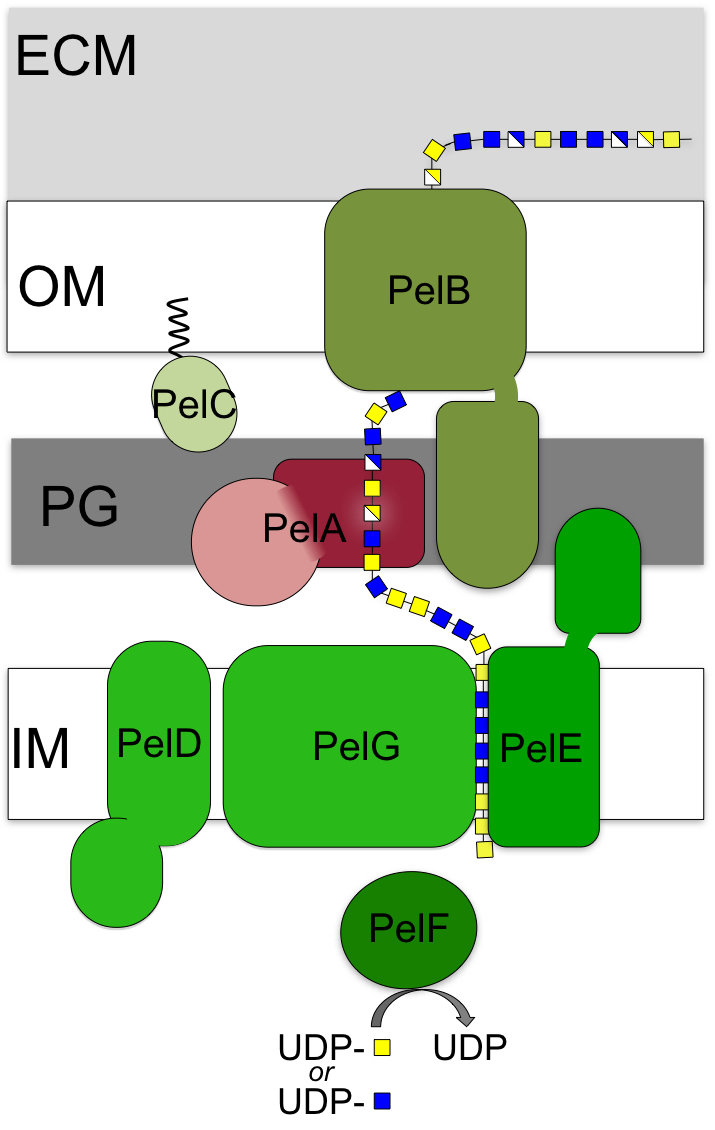
In addition to mucoid P. aeruginosa strains, strains with a wrinkly small colony morphology and increased biofilm forming capacity have been isolated from CF sputum. These strains have increased expression of the Psl and Pel polysaccharides, and suggest that all three exopolysaccharides, alginate, Psl and Pel, play important roles in the colonization and maintenance of CF lung infections. Pel and Psl are the predominant polysaccharides found in biofilm infections in other clinical and all environmental settings, where together or individually they act as adhesins to maintain biofilm structure. Pel is a cationic polymer composed of 1,4 linked N-acetylglucosamine and N-acetylgalactosamine. Pel has been shown to initiate and maintain cell-to-cell interactions, and provide resistance to aminoglycoside antibiotics.
At present, our understanding of the molecular processes used by the seven proteins encoded on the pelABCDEFG operon to produce Pel is relatively limited. Our studies have shown that PelA is a multi-domain protein with both de-N-acetylase and hydrolase activities, and that while Pel polymerization, like alginate, is regulated by c-di-GMP, the inner membrane protein PelD uses a degenerate GGDEF domain rather than a PilZ domain (left).
Current projects
Our current projects are focused on:
- Characterizing the role of the outer membrane lipoprotein PelC.
- Determining how the polymer is exported via the multi-domain protein PelB.
- Determining whether the proteins interact to form a multi-protein complex or complexes and characterizing these interactions.
- Developing PelA as a therapeutic for the prevention and degradation of Pel-dependent biofilms.
- Identifying small molecule modulators of PelA deacetylase activity.
Selected Publications
-
PelA and PelB proteins form a modification and secretion complex essential for Pel polysaccharide-dependent biofilm formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Marmont LS, Whitfield GB, Rich JD, Yip P, Giesbrecht LB, Stremick CA, Whitney JC, Parsek MR, Harrison JJ, Howell PL. J Biol Chem. 2017 Nov 24;292(47):19411-19422. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.812842.
-
Oligomeric lipoprotein PelC guides Pel polysaccharide export across the outer membrane of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Marmont LS, Rich JD, Whitney JC, Whitfield GB, Almblad H, Robinson H, Parsek MR, Harrison JJ, Howell PL. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Mar 14;114(11):2892-2897. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1613606114.
-
Pel is a cationic exopolysaccharide that cross-links extracellular DNA in the Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm matrix. Jennings LK, Storek KM, Ledvina HE, Coulon C, Marmont LS, Sadovskaya I, Secor PR, Tseng BS, Scian M, Filloux A, Wozniak DJ, Howell PL, Parsek MR. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Sep 8;112(36):11353-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1503058112.
-
Enzymatic modifications of exopolysaccharides enhance bacterial persistence. Whitfield GB, Marmont LS, Howell PL. Front Microbiol. 2015 May 15;6:471. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2015.00471.
- Structure of the cytoplasmic region of PelD, a degenerate diguanylate cyclase receptor that regulates exopolysaccharide production in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Whitney JC, Colvin KM, Marmont LS, Robinson H, Parsek MR, Howell PL. J Biol Chem. 2012 Jul 6;287(28):23582-93. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.375378.