Browse our PubMed for a complete list of publications. Below are a few summaries of recent studies conducted in the Brumell lab.
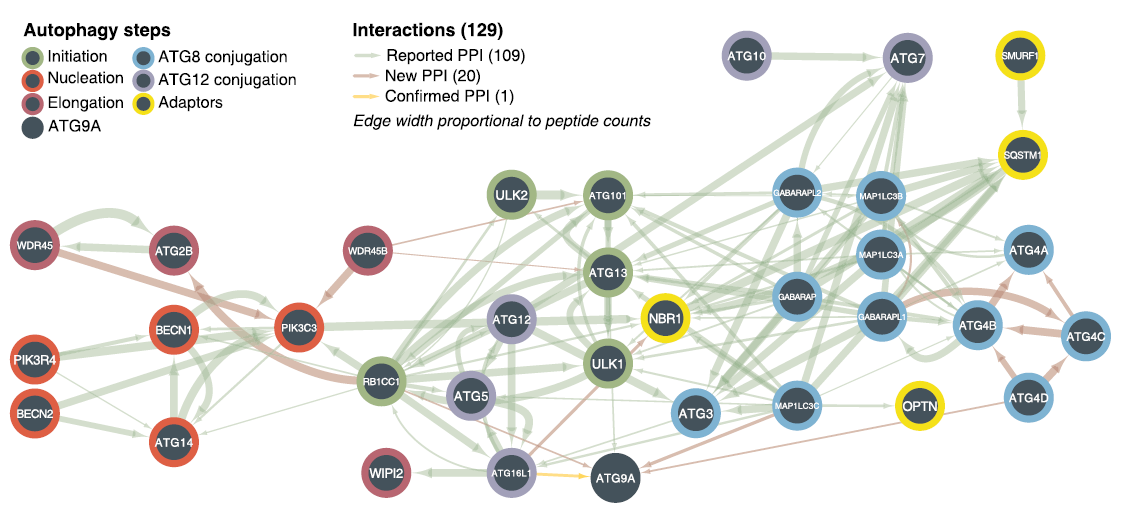
In this publication we use advanced proteomics to examine the autophagy pathway. Our findings reveal many new connections of autophagy to essential cellular pathways. We also identify a new role for members of the OSBPL family of lipid transport proteins in autophagy.
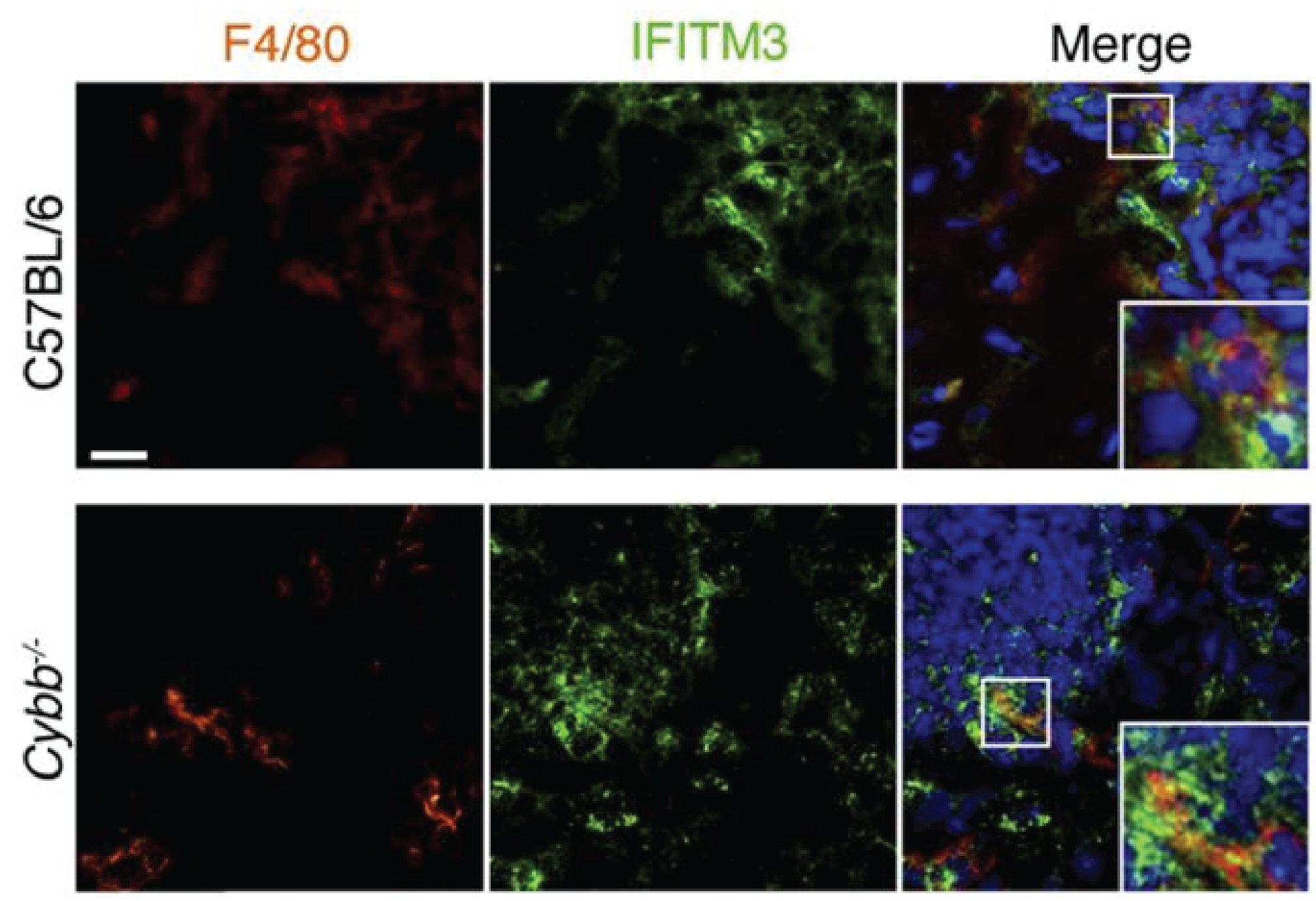
The NOX2 NADPH oxidase was previously thought to control bacterial infection through the production of reactive oxygen species. In this publication we show that this oxidase control Listeria monocytogenes infection indirectly, through the regulation of an antiviral response.
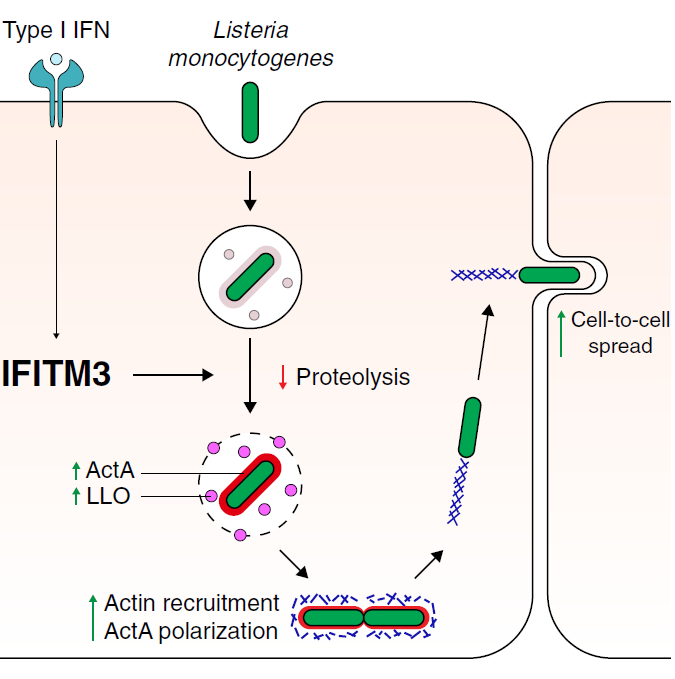
Our cells fight viral infection using a group of proteins that can target specific steps in the viral processes. IFITM3 is one such protein, and plays a key role in protecting us from many viruses, including the flu and COVID-19. In this publication we show that the bacterial pathogen Listeria monocytogenes can take advantage of IFITM3 during its infection of host cells.