Publications
Insight into our projects and continued progress
Highlighted publications
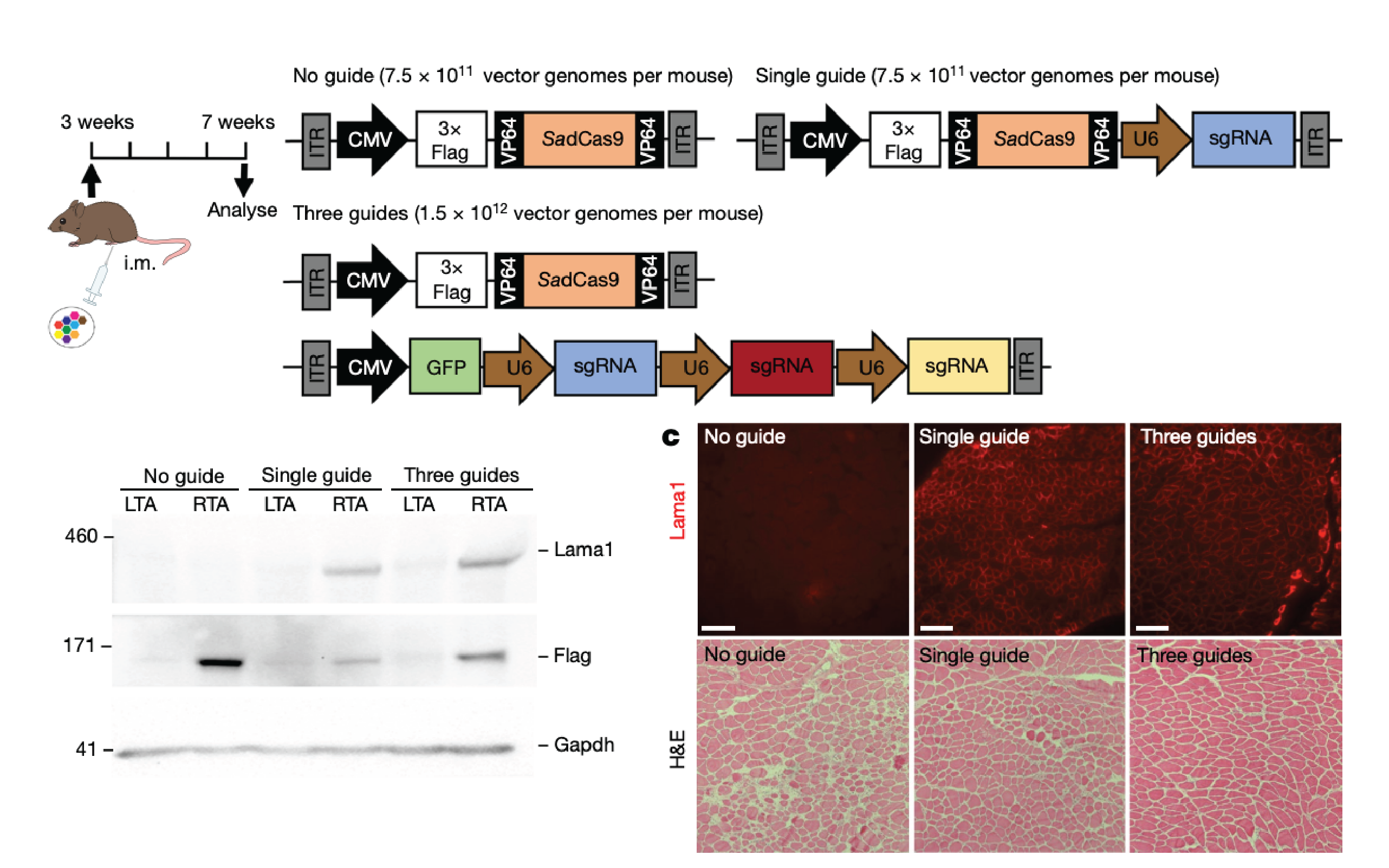
A mutation-independent approach for muscular dystrophy via upregulation of a modifier gene
Here, we report a mutation-independent strategy to upregulate the expression of a disease-modifying gene associated with congenital muscular dystrophy type 1A (MDC1A) using the CRISPR activation system in mice.
We modulated expression of Lama1 in a mouse model of MDC1A using an adeno-associated virus (AAV9) carrying a catalytically inactive Cas9 (dCas9), VP64 transactivators and single-guide RNAs that target the Lama1 promoter.
Our data demonstrated the feasibility and therapeutic benefit of CRISPR-dCas9-mediated upregulation of Lama1, which may enable mutation-independent treatment for all patients with MDC1A. This approach has a broad applicability to a variety of disease-modifying genes and could serve as a therapeutic strategy for many inherited and acquired diseases.
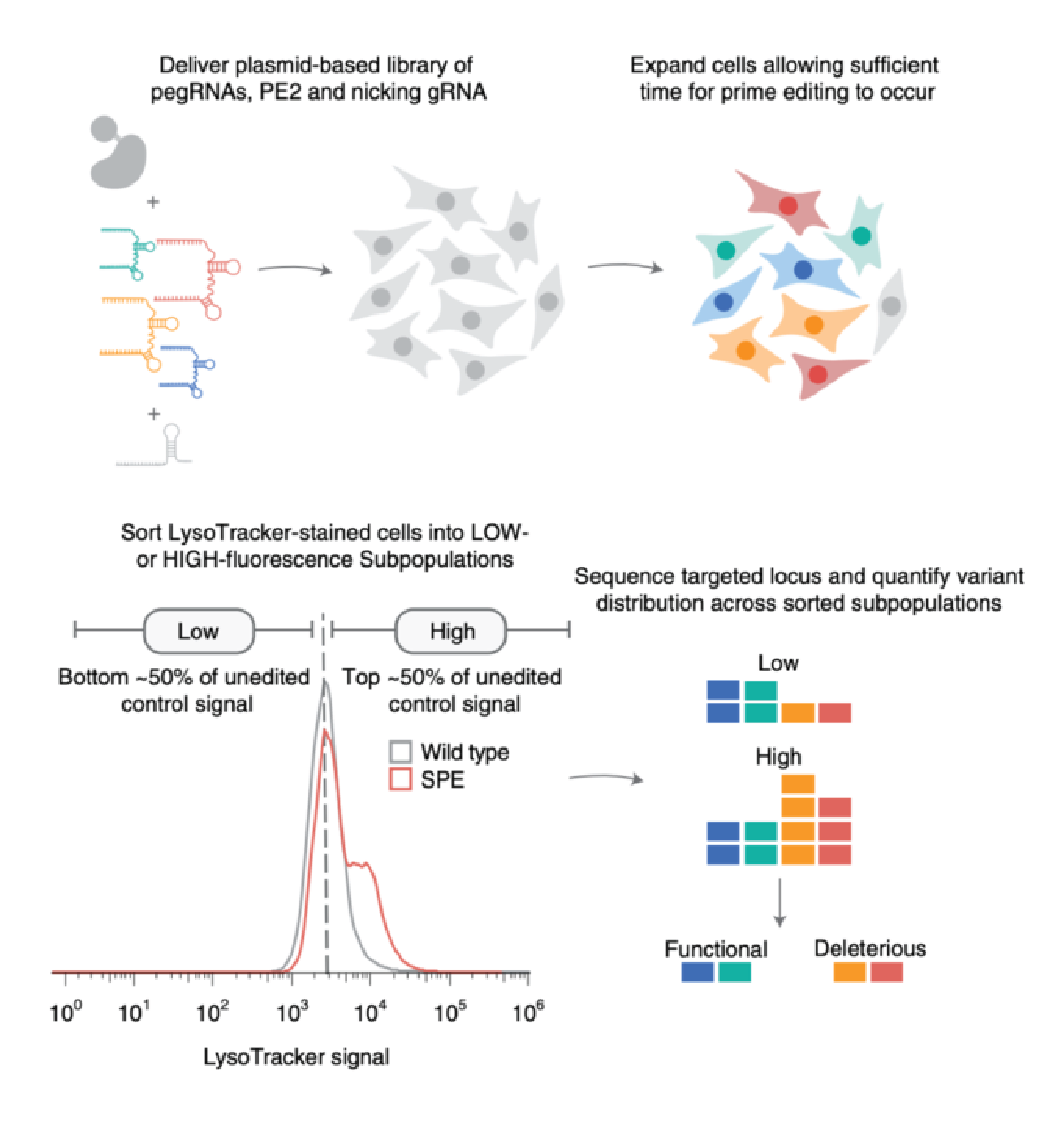
Saturation variant interpretation using CRISPR prime editing
Here, we adapted CRISPR prime editing for high-throughput variant classification and combined it with a strategy that allows for haploidization of any locus, which simplifies variant interpretation.
We demonstrate the utility of saturation prime editing (SPE) by applying it to the NPC intracellular cholesterol transporter 1 gene (NPC1), mutations in which cause the lysosomal storage disorder Niemann–Pick disease type C.
In sum, we show that SPE allows for efficient, accurate functional characterization of genetic variants
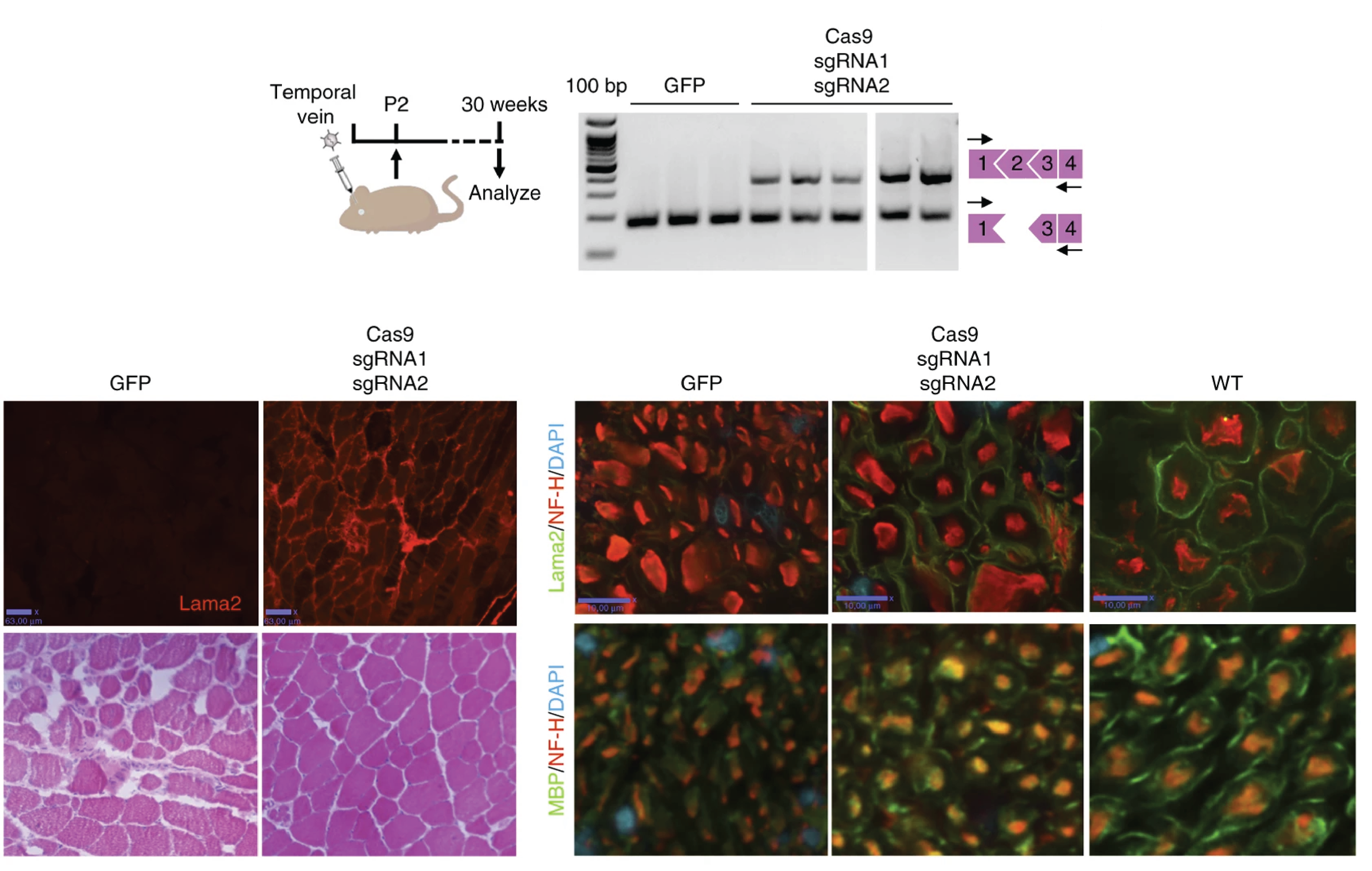
Correction of a splicing defect in a mouse model of congenital muscular dystrophy type 1A using a homology-directed-repair-independent mechanism
Here, we correct a splice-site mutation that causes the exclusion of exon 2 from Lama2 mRNA and the truncation of Lama2 protein in a mouse model of MDC1A.
Through systemic delivery of adeno-associated virus (AAV) carrying clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR)-Cas9 genome-editing components, we simultaneously excise an intronic region containing the mutation and create a functional donor splice site through NHEJ.
This strategy leads to the inclusion of exon 2 in the Lama2 transcript and restoration of full-length Lama2 protein. Results also displayed substantial improvement in muscle histopathology and function without signs of paralysis.
All publications
View all of our recent publications listed chronologically
2025
Mollica A, Omer S, Forguson G, Steiman S, Evagelou SL, Naumenko S, Walker S, Li LY, Teeling A, Lindsay K, Erwood S. Mutations in the β-tubulin TUBB impair ciliogenesis and are associated with ciliopathy-like phenotypes. Nature Communications. 2025 Nov 27;16(1):10637.
Hung, J. E., Brewer, R. A., Elbakr, L., Mollica, A., Forguson, G., Chan, W. S., & Ivakine, E. A. (2024). Precise template-free correction restores gene function in Tay-Sachs disease while reframing is ineffective. Molecular Therapy-Nucleic Acids, 36(1).
2024
Rizvi, S. Z., Chan, W. S., Maino, E., Steiman, S., Forguson, G., Klepfish, M., … & Ivakine, E. A. (2024). Multi-gene duplication removal in an engineered human cellular MECP2 duplication syndrome model with an IRAK1-MECP2 duplication. Molecular Therapy-Nucleic Acids, 35(4) e102356.
Maino E, Scott O, Rizvi SZ, Chan WS, Visuvanathan S, Zablah YB, Li H, Sengar AS, Salter MW, Jia Z, Rossant J, Cohn RD, Gu B, Ivakine EA. (2024). A Cas9-fusion proximity-based approach generates an Irak1-Mecp2 tandem duplication mouse model for the study of MeCP2 duplication syndrome. Disease Models & Mechanisms, Epub ahead of print PMID 38881329.
2023
Scott, O., Visuvanathan, S., Reddy, E., Mahamed, D., Gu, B., Roifman, C. M., Cohn, R. D., Guidos, C. J., & Ivakine, E. A. (2023). The human Stat1 gain-of-function T385M mutation causes expansion of activated T-follicular helper/T-helper 1-like CD4 T cells and sex-biased autoimmunity in specific pathogen-free mice. Frontiers in immunology, 14, 1183273.
Tillotson, R., Yan, K., Ruston, J., de Young, T., Córdova, A., Turcotte-Cardin, V., Yee, Y., Taylor, C., Visuvanathan, S., Babbs, C., Ivakine, E. A., Sled, J. G., Nieman, B. J., Picketts, D. J., & Justice, M. J. (2023). A new mouse model of ATR-X syndrome carrying a common patient mutation exhibits neurological and morphological defects. Human molecular genetics, ddad075. Advance online publication.
2022
Schultz, M. L., Schache, K. J., Azaria, R. D., Kuiper, E. Q., Erwood, S., Ivakine, E. A., Farhat, N. Y., Porter, F. D., Pathmasiri, K. C., Cologna, S. M., Uhler, M. D., & Lieberman, A. P. (2022). Species-specific differences in NPC1 protein trafficking govern therapeutic response in Niemann-Pick type C disease. JCI insight, 7(23), e160308.
Teng, A. C. T., Tavassoli, M., Shrestha, S., Marks, R. M., McFadden, M. J., Evagelou, S. L., Lindsay, K., Vandenbelt, A., Li, W., Ivakine, E., Cohn, R., Santerre, J. P., & Gramolini, A. O. (2022). An efficient and cost-effective purification protocol for Staphylococcus aureus Cas9 nuclease. STAR protocols, 4(1), 101933. Advance online publication.
Fatehi, S., Marks, R. M., Rok, M. J., Perillat, L., Ivakine, E. A., & Cohn, R. D. (2023). Advances in CRISPR/Cas9 Genome Editing for the Treatment of Muscular Dystrophies. Human gene therapy, 34(9-10), 388–403.
Erwood, S., Bily, T. M. I., Lequyer, J., Yan, J., Gulati, N., Brewer, R. A., Zhou, L., Pelletier, L., Ivakine, E. A., & Cohn, R. D. (2022). Saturation variant interpretation using CRISPR prime editing. Nature biotechnology, 40(6), 885–895.
2021
Maino, E., Wojtal, D., Evagelou, S. L., Farheen, A., Wong, T. W. Y., Lindsay, K., Scott, O., Rizvi, S. Z., Hyatt, E., Rok, M., Visuvanathan, S., Chiodo, A., Schneeweiss, M., Ivakine, E. A., & Cohn, R. D. (2021). Targeted genome editing in vivo corrects a Dmd duplication restoring wild-type dystrophin expression. EMBO molecular medicine, 13(5), e13228.
Scott, O., Lindsay, K., Erwood, S., Mollica, A., Roifman, C. M., Cohn, R. D., & Ivakine, E. A. (2021). STAT1 gain-of-function heterozygous cell models reveal diverse interferon-signature gene transcriptional responses. NPJ genomic medicine, 6(1), 34.
Shrestha, S., McFadden, M. J., Teng, A. C. T., Chang, P. D. M., Deng, J., Wong, T. W. Y., Cohn, R. D., Ivakine, E. A., Gramolini, A. O., & Santerre, J. P. (2021). Self-Assembled Oligo-Urethane Nanoparticles: Their Characterization and Use for the Delivery of Active Biomolecules into Mammalian Cells. ACS applied materials & interfaces, 13(49), 58352–58368.
2020
Erwood, S., Laselva, O., Bily, T. M. I., Brewer, R. A., Rutherford, A. H., Bear, C. E., & Ivakine, E. A. (2020). Allele-Specific Prevention of Nonsense-Mediated Decay in Cystic Fibrosis Using Homology-Independent Genome Editing. Molecular therapy. Methods & clinical development, 17, 1118–1128.
Wong, T. W. Y., Ahmed, A., Yang, G., Maino, E., Steiman, S., Hyatt, E., Chan, P., Lindsay, K., Wong, N., Golebiowski, D., Schneider, J., Delgado-Olguín, P., Ivakine, E. A., & Cohn, R. D. (2020). A novel mouse model of Duchenne muscular dystrophy carrying a multi-exonic Dmd deletion exhibits progressive muscular dystrophy and early-onset cardiomyopathy. Disease models & mechanisms, 13(9), dmm045369.
2019
Kemaladewi, D. U., Bassi, P. S., Erwood, S., Al-Basha, D., Gawlik, K. I., Lindsay, K., Hyatt, E., Kember, R., Place, K. M., Marks, R. M., Durbeej, M., Prescott, S. A., Ivakine, E. A., & Cohn, R. D. (2019). A mutation-independent approach for muscular dystrophy via upregulation of a modifier gene. Nature, 572(7767), 125–130.
Laselva, O., Erwood, S., Du, K., Ivakine, Z., & Bear, C. E. (2019). Activity of lumacaftor is not conserved in zebrafish Cftr bearing the major cystic fibrosis-causing mutation. FASEB bioAdvances, 1(10), 661–670.
Mennesson, M., Rydgren, E., Lipina, T., Sokolowska, E., Kulesskaya, N., Morello, F., Ivakine, E., Voikar, V., Risbrough, V., Partanen, J., & Hovatta, I. (2019). Kainate receptor auxiliary subunit NETO2 is required for normal fear expression and extinction. Neuropsychopharmacology : official publication of the American College of Neuropsychopharmacology, 44(11), 1855–1866.
Erwood, S., Brewer, R. A., Bily, T. M. I., Maino, E., Zhou, L., Cohn, R. D., & Ivakine, E. A. (2019). Modeling Niemann-Pick disease type C in a human haploid cell line allows for patient variant characterization and clinical interpretation. Genome research, 29(12), 2010–2019.
2018
Kemaladewi, D. U., Benjamin, J. S., Hyatt, E., Ivakine, E. A., & Cohn, R. D. (2018). Increased polyamines as protective disease modifiers in congenital muscular dystrophy. Human molecular genetics, 27(11), 1905–1912.
2017
Kemaladewi, D. U., Maino, E., Hyatt, E., Hou, H., Ding, M., Place, K. M., Zhu, X., Bassi, P., Baghestani, Z., Deshwar, A. G., Merico, D., Xiong, H. Y., Frey, B. J., Wilson, M. D., Ivakine, E. A., & Cohn, R. D. (2017). Correction of a splicing defect in a mouse model of congenital muscular dystrophy type 1A using a homology-directed-repair-independent mechanism. Nature medicine, 23(8), 984–989.